About
Hello 👋 I am currently a Postdoctoral Fellow at the
Smart Systems Institute, National University of Singapore,
under the supervision of Prof. Harold Soh.
Before that, I obtained my PhD from the
Language Technology Research Center, Faculty of Computing,
Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT), where I was co-supervised
by Prof. Yi Guan and
Prof. Jingchi Jiang.
I was also a visiting PhD student in the Autonomous Agents Research Group at the University of Edinburgh (UoE), supervised by Prof. Stefano V. Albrecht.
I'm on my mission to build our robotic friends 🤖. In my research, my research focuses on Embodied AI safety and inference-time alignment for diffusion models. Back in my PhD days, I developed deep reinforcement-learning algorithms for autonomous agents, with a particular emphasis on RL generalisation and causal RL.
News
📢 2025.3 I successfully defended my viva 🥳
📢 2024.9 One paper accepted by 🔥 NeurIPS 2024 🔥
📢 2024.8 I have completed my one-year visit at the Autonomous Agents Research Group, and I’ve collected many precious memories in Edinburgh. All the best to my lovely friends and colleagues 💕
📢 2024.6 I am luck to organise an academic exchange for the Agent group to major institutions in China, including Tsinghua University, Peking University, and others. For more details, please see: Twitter !! See you all there 👋
📢 2023.2 I am delighted that my work [2] [6] has been deployed in the WI Healthcare System, which is now serving doctors and patients in two hospitals 🏥, as reported by WWW.CHINANEWS.COM
Education

|
University of Edinburgh - (2023-2024)
Project: Skill-aware Mutual Information Optimisation for Generalisation in Reinforcement Learning
I was a visiting student in the Autonomous Agents Research Group at the University of Edinburgh, supervised by Prof. Stefano V. Albrecht.
|

|
Harbin Institute of Technology - (2019-2025)
Thesis: Causal Reinforcement Learning Generalisation for Healthcare Agents
I began my doctoral studies directly following my undergraduate degree, thanks to the postgraduate recommendation scheme. I am currently pursuing a PhD at the Faculty of Computing at Harbin Institute of Technology.
GPA: 92.53/100
|

|
Harbin Engineering University - (2015-2019)
I earned my bachelor’s degree in Internet of Things Engineering from the College of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Engineering University in 2019. I was honoured the Outstanding Graduates and Outstanding Graduation Thesis in 2019.
GPA: 88.95/100.
|
Work Experience

|
Research Intern @ Beijing Institute for General Artificial Intelligence (BIGAI) - (2025)
Research on learning from offline expert datasets (human demonstrations and cross-embodiment datasets) for robot manipulation.Research on learning from offline expert datasets (human demonstrations and cross-embodiment datasets) for robot manipulation.
|
Selected Publication
|
[1] Skill-aware Mutual Information Optimisation for Generalisation in Reinforcement Learning
Xuehui Yu, Mhairi Dunion, Xin Li, Stefano V Albrecht
NeurIPS 2024
Keywords: contrastive learning, RL, meta RL, zero-shot generalisation.
❓ How to build general robots capable of seamlessly operating in any environment, with any object, and utilising various skills?
With our SaMI learning objective, RL agents are incentivised to become versatile and zero-shot generalise across infinite tasks 😉
💡 Generalisation starts with corrective behaviors. The ability to correct and try again is likely a key ingredient.
Code | Paper | Our benchmark: Sa-Panda-gym | SlidesLive demo video
|

|
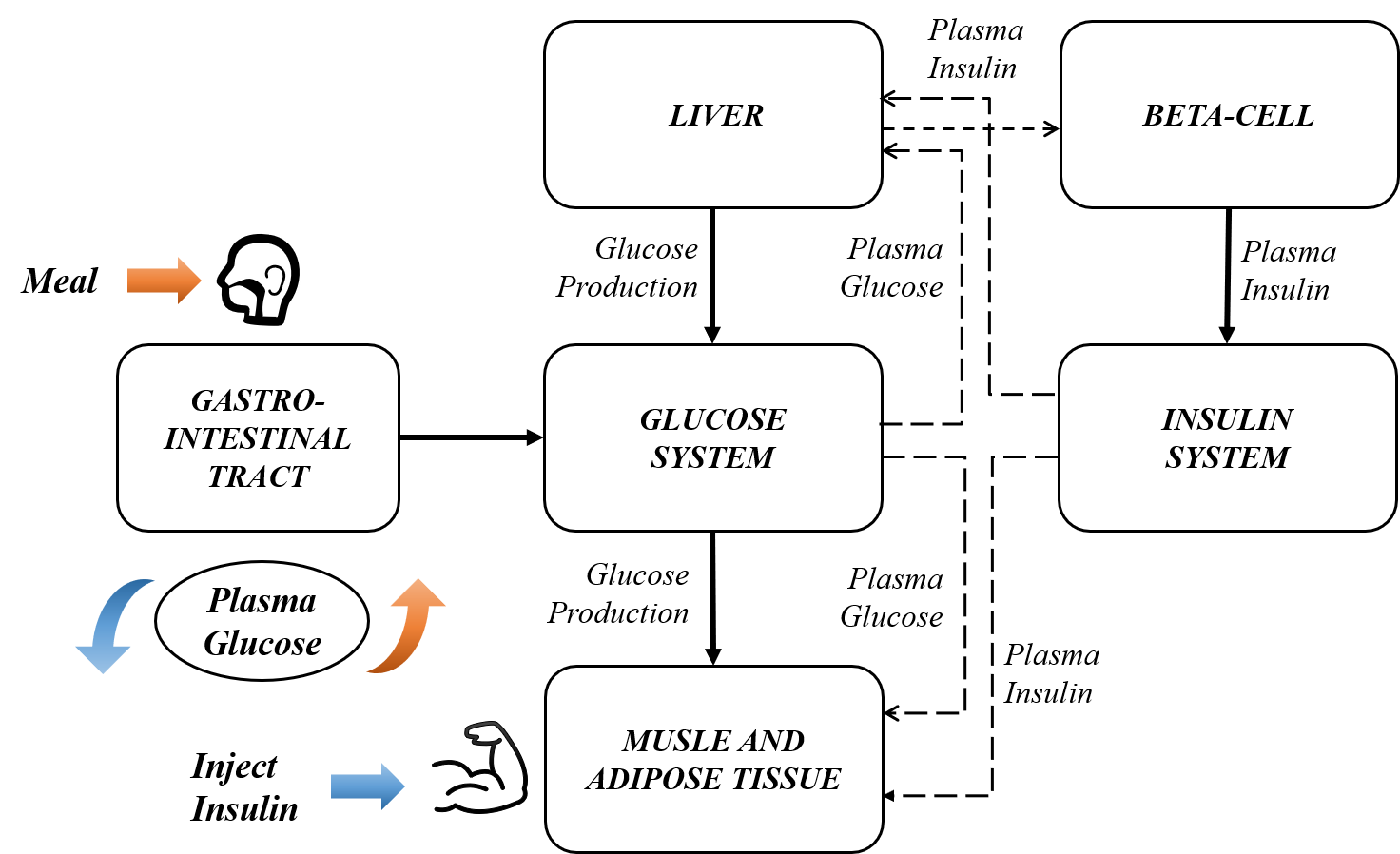
[2] ARLPE: A Meta Reinforcement Learning Framework for Glucose Regulation in Type 1 Diabetics
Xuehui Yu, Yi Guan, Lian Yan, Shulang Li, Xuelian Fu, Jingchi Jiang*
Expert Systems With Applications, IF: 8.665.
Keywords: meta-RL, active learning, fast online adaptation, RL generalisation.
❓ How can rapid adaptation be achieved with extremely limited data in an online deployment? Employ “optimistic exploration” through active RL!
💉 A RL-based closed-loop control method for artificial pancreas systems, enabling automatic medication infusion via pump control for diverse, previously unseen clinical patients.
Code | Paper| WI Healthcare APP
|
|
[3] Causal Coupled Mechanisms: A Control Method with Cooperation and Competition for Complex System
Xuehui Yu, Jingchi Jiang, Xinmiao Yu, Yi Guan*, Xue Li
The (BIBM) 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine.
Keywords: hierarchical RL, transfer learning, skill composition, RL generalisation.
💡 Using inductive biases to encourage or ensure the model does not rely on features that we expect to change: The policy should only rely on features which will behave similarly in both the training and testing environments.
Paper
|

|
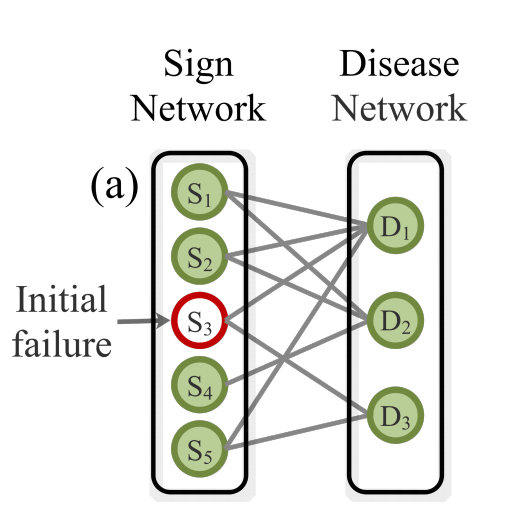
[4] PercolationDF: A percolation-based medical diagnosis framework
Jingchi Jiang, Xuehui Yu, Yi Lin, Yi Guan
Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2022, 19(6): 5832-5849.
Keywords: medical diagnosis, knowledge representation.
The dynamic model based on cascading theory, which models the physiological domino effect in environment dynamics; Increasing similarity between training and testing for generalisation in class-imbalanced datasets.
Paper
|
|
[5] DECAF: An Interpretable Deep Cascading Framework for ICU Mortality Prediction
Jingchi Jiang, Xuehui Yu, Boran Wang, Linjiang Ma, Yi Guan
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (2022): 102437.
Keywords: graph attention networks, spatio-temporal forecasting, interpretability, mortality prediction.
The dynamic model based on cascading theory, which models the physiological domino effect in environment dynamics; Increasing similarity between training and testing for generalisation in class-imbalanced datasets.
Paper
|
Awards & Honours
- 2023 World’s Top Universities Strategic Cooperation Fellowship Initiative
- 2023 and 2019 Heilongjiang Province Merit Student
- 2018 National Scholarship
- Awarded to 140 students school-wide in 2018, about 1%
- 2018 Pacemaker to Merit Student
- Only 10 selected school-wide each year
- 2017 China Undergraduate Mathematical Contest in Modeling, National Second Prize;
- Problem A: CT System Parameter Calibration and Imaging
- Addressed calibration challenges in CT systems, where installation errors impact imaging quality.
- Developed methods to calibrate system parameters using known structured samples (templates) and applied these parameters to image unknown samples.
- 2017 Northeast Three Provinces Mathematical Contest in Modeling, Provincial Third Prize
- 14th 'Bochuang Cup' National College Student Embedded System Design Contest, Provincial Third Prize
- Project: Kindergarten Safety Protection System
- Developed a system leveraging multiple sensors to monitor children’s activities, detect unusual behaviours, and identify potential risks.
- Enabled timely alerts to caregivers and teachers, facilitating swift responses and creating a safer environment for children.
- Heilongjiang Province 5th College Students Art Performance, Vocal Music Category A, Third Prize 🎶
Random
|